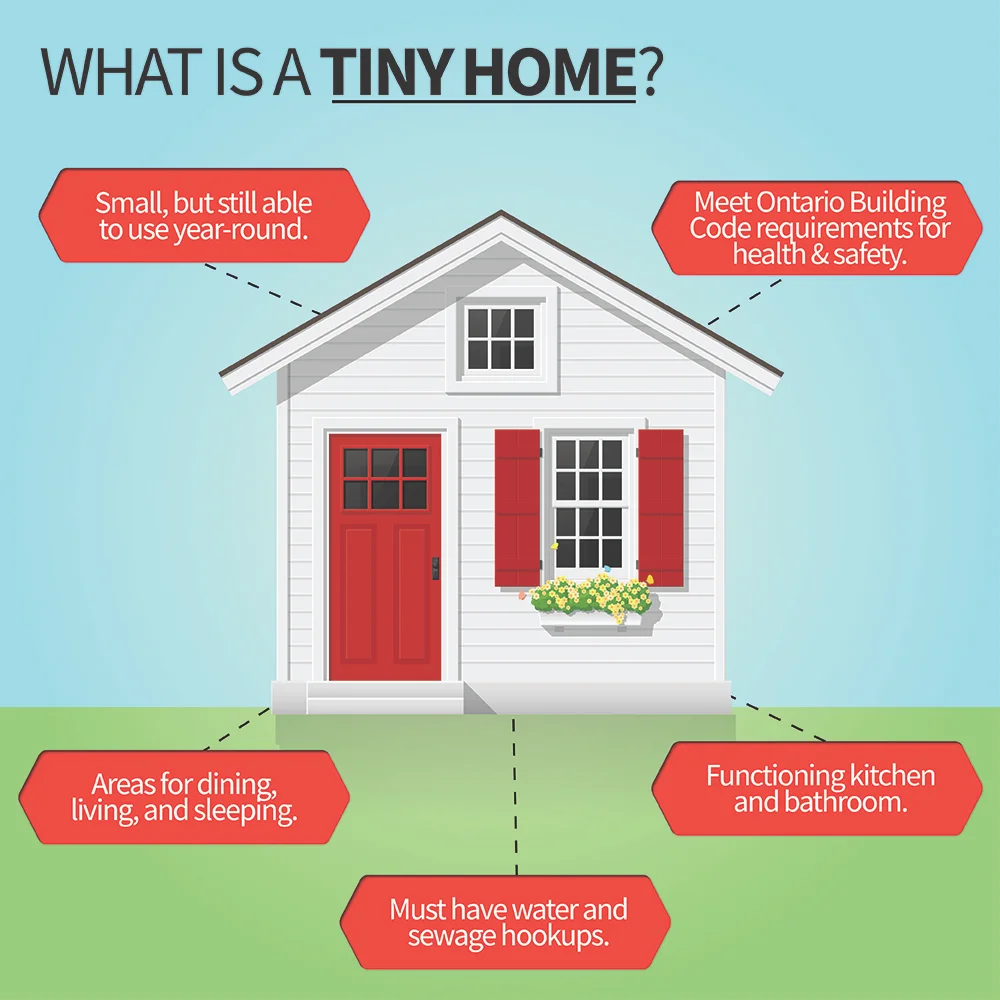
Are you considering building a tiny home but unsure if there are building codes in place for such unique structures? Rest assured, there are building codes specifically designed for tiny homes. These codes ensure that your tiny home is structurally sound, safe, and up to standard. In this article, we will explore the importance of building codes for tiny homes and how they can help you in creating your dream living space. So, whether you’re planning to downsize or want to embrace a minimalist lifestyle, understanding and following building codes is crucial to ensure a successful and compliant construction process.

Overview of Tiny Homes
Different types of tiny homes
Tiny homes come in various forms, each offering its own unique advantages and challenges. Some common types of tiny homes include tiny houses on wheels (THOWs), which are built on trailers and offer flexibility in terms of mobility. Other options include small cottages or cabins, container homes converted from shipping containers, and backyard tiny houses. Each type of tiny home comes with its own set of considerations for construction and living arrangements.
Unique challenges of building and living in tiny homes
While living in a tiny home can provide a simpler and more sustainable lifestyle, there are certain challenges that come with it. Building a tiny home requires careful planning and design to maximize space utilization and ensure structural integrity. Additionally, living in a small space requires a deliberate approach to organization and storage to make the most of the limited square footage. Adequate ventilation, insulation, and privacy are also important factors to consider in tiny home living.
Importance of Building Codes
Ensuring safety and structural integrity
Building codes play a crucial role in ensuring that homes meet minimum safety standards and are structurally sound. These codes outline requirements for materials, construction techniques, and design elements that are necessary to protect occupants from hazards and potential building failures. By adhering to building codes, builders and homeowners can have confidence in the safety and durability of their tiny homes.
Consistency and standardization
Building codes provide a uniform set of standards that all builders must follow. This consistency helps to ensure that homes are built to a certain level of quality, regardless of geographical location. By setting common guidelines for construction, building codes improve the overall consistency and reliability of housing, including tiny homes.
Addressing health and environmental concerns
Building codes also consider factors related to health and environmental concerns. This includes guidelines for insulation, ventilation, and energy efficiency to promote occupant well-being and reduce environmental impact. By incorporating sustainability principles into building codes, tiny homes can become even more eco-friendly and energy-efficient.
Understanding Building Codes
Definition and purpose of building codes
Building codes are a set of regulations and standards established by local, state, or national authorities that dictate how buildings should be constructed. Their primary purpose is to protect the health, safety, and welfare of the occupants and the community at large. Building codes cover a wide range of areas, including structural integrity, fire safety, plumbing, electrical systems, and energy efficiency.
Role of building codes in the construction industry
Building codes serve as a critical foundation for the construction industry. They provide a framework of minimum requirements that builders must meet, ensuring that buildings are safe, reliable, and in compliance with the law. Building codes also help to level the playing field by setting a standard that all builders must adhere to, regardless of their size or experience.
Code development and adoption process
Building codes are typically developed and administered by government entities at the local, state, or national level. The process of creating and adopting building codes involves input from various stakeholders, including experts, industry professionals, and the public. Codes are regularly updated to incorporate advancements in technology, materials, and industry best practices.
Building Codes for Tiny Homes
Inclusion of tiny homes in existing building codes
Tiny homes are often subject to the same building codes as traditional homes, with some modifications to address their unique characteristics. While not all jurisdictions have specific provisions for tiny homes, many include them under existing codes for dwellings. However, it is essential for builders and homeowners to familiarize themselves with the specific requirements and any exemptions or modifications that apply to tiny homes in their respective areas.
Variation in codes across different jurisdictions
Building codes can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. This means that what is acceptable in one area may not meet the requirements in another. This variation poses a challenge for those building and living in tiny homes, especially if they plan to relocate. It is crucial to research and understand the local building codes and regulations before starting any construction project.
Specific requirements for tiny homes
While building codes for tiny homes may be similar to those for larger homes, there are some specific requirements that cater to the unique characteristics of tiny homes. These requirements often revolve around size limitations, mobility, and access to utilities. For example, tiny homes on wheels may need to comply with additional regulations for trailers or mobile homes. Additionally, zoning restrictions may dictate where tiny homes can be located and the duration of their occupancy.

Regulation and Zoning
Necessary permits and inspections
Just like traditional homes, tiny homes require permits and inspections during the construction process to ensure compliance with building codes. These permits may include building permits, electrical permits, plumbing permits, and more, depending on the jurisdiction. Inspections are typically conducted at various stages of construction to verify compliance with the applicable codes and regulations.
Zoning regulations for tiny homes as permanent dwellings
Zoning regulations determine the land use designation and allowable uses in different areas. When it comes to tiny homes as permanent dwellings, zoning regulations may impose specific requirements on minimum lot size, setbacks, and density. Some areas may have zoning restrictions that classify tiny homes as accessory dwelling units (ADUs), limiting their use to certain zones. It is important to research and understand the zoning regulations in a given area to ensure compliance and avoid future complications.
Temporary use and parking considerations
For those who choose to live in tiny homes on a temporary basis, such as during vacation or as a temporary dwelling, additional considerations come into play. Some jurisdictions allow for temporary use permits that enable individuals to place their tiny homes on specific properties for a limited duration. Parking requirements and options for temporary dwellings are also important factors to consider, as not all areas may allow for tiny home parking or have suitable infrastructure in place.
Common Building Code Requirements
Minimum size and square footage regulations
Many building codes specify minimum size requirements for habitable spaces, including bedrooms, living areas, and kitchens. These requirements aim to ensure that spaces are adequate for human occupancy and promote a reasonable standard of livability. In the context of tiny homes, meeting these minimum size requirements can be challenging, as they may conflict with the goal of maximizing space utilization in a limited footprint.
Structural requirements for stability and durability
Building codes provide guidelines for structural elements, such as foundations, walls, and roofs, to ensure stability and durability. These requirements typically address factors like material strength, load-bearing capacities, and seismic considerations. Adhering to these structural requirements is essential in tiny homes, as their compact size may make them more susceptible to certain structural vulnerabilities.
Fire safety regulations
Building codes include provisions for fire safety, including requirements for smoke detectors, fire-resistant materials, and accessible emergency exits. These regulations are crucial in protecting occupants and preventing the spread of fires. In small spaces like tiny homes, it is essential to carefully consider fire safety measures, such as using fire-resistant building materials and providing multiple means of egress.
Energy efficiency standards
In an era of increasing environmental concerns, building codes are evolving to include energy efficiency standards. These standards aim to reduce the environmental impact of buildings and promote sustainable practices. Tiny homes, with their smaller size, have the potential to be highly energy-efficient. By following energy efficiency standards outlined in building codes, tiny home builders can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Plumbing, electrical, and HVAC requirements
Building codes stipulate requirements for plumbing, electrical systems, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to ensure functionality and safety. These requirements encompass aspects such as plumbing fixture counts, electrical wiring standards, and HVAC system sizing. Adhering to these codes ensures that essential utilities are provided safely and efficiently within a tiny home.

Challenges in Code Compliance
Adapting and customizing existing codes for tiny homes
One of the main challenges in code compliance for tiny homes is adapting existing building codes to accommodate their unique characteristics. Given their smaller size, mobility, and different construction methods, tiny homes may require specific code modifications or exemptions. The process of achieving code compliance may involve working closely with local authorities to propose and implement changes that reflect the unique needs of tiny homes.
Affordability and accessibility concerns
Tiny homes are often built as more affordable housing options, but the cost of compliance with building codes can pose financial challenges. Meeting stringent standards, such as energy efficiency requirements, might require additional investments in materials and technologies. Additionally, ensuring accessibility for people with disabilities can present additional compliance challenges that may impact the affordability of tiny homes.
Code enforcement challenges
Enforcing building codes for tiny homes can be challenging due to their unique characteristics and the potential for non-traditional construction methods. Local authorities may need to build specialized knowledge and expertise to effectively enforce the codes specific to tiny homes. Collaborative efforts between builders, homeowners, and regulatory agencies are crucial to ensure ongoing compliance and address any enforcement challenges that may arise.
Certification and Inspection
Certification programs for tiny homes
Certification programs specific to tiny homes have emerged to help ensure quality and compliance with building codes. These programs provide a way for builders to demonstrate that their tiny homes meet certain standards of safety, durability, and energy efficiency. By obtaining certification, builders can offer potential homeowners peace of mind and assurance that their tiny homes have been thoroughly inspected and meet recognized industry standards.
Importance of third-party inspections
Third-party inspections play a vital role in ensuring code compliance for tiny homes. These inspections are conducted by independent professionals who have expertise in building codes and regulations. By having a neutral third party inspect the construction process and the final product, the risk of potential conflicts of interest or oversights is reduced, and a higher level of accountability is achieved.
Ensuring compliance with building codes
Compliance with building codes should be a priority for both builders and homeowners of tiny homes. Adhering to these codes helps to ensure the safety, durability, and efficiency of tiny homes. Builders should follow best practices, engage in ongoing education about codes, and seek professional guidance when needed. Homeowners, on the other hand, should make sure that any modifications or additions to their tiny homes also comply with the applicable building codes.

Building Code Resources
Online resources for building codes
Several online resources provide access to building codes and related information. These resources often include searchable databases, code libraries, and educational materials to help builders, homeowners, and professionals navigate the complex world of building codes. Websites such as the International Code Council (ICC), National Association of Home Builders (NAHB), and local government websites are valuable sources of information on building codes for tiny homes.
Organizations and professionals specializing in tiny home codes
As the popularity of tiny homes continues to grow, so does the number of organizations and professionals specializing in tiny home codes. These organizations offer expertise and guidance to builders and homeowners, ensuring compliance with building codes and addressing any challenges unique to tiny homes. Working with professionals who understand the intricacies of tiny home construction can help ensure that all code requirements are met and that the construction process goes smoothly.
Innovations in Tiny Home Codes
Proposed changes and amendments for tiny homes
Recognizing the growing demand for tiny homes, there have been proposals for changes and amendments to existing building codes to better accommodate this alternative housing option. These changes may include specific provisions for tiny homes, such as size exemptions, mobility requirements, and variances for zoning restrictions. Advocacy groups and industry professionals continue to push for these changes to support the development of safe and sustainable tiny homes.
Advancements in sustainable construction practices
Building codes are constantly evolving to incorporate advancements in sustainable construction practices. This includes guidelines for using eco-friendly materials, implementing energy-efficient systems, and incorporating renewable energy sources. These advancements align well with the goals of tiny home living, making it easier for builders and homeowners to create environmentally-friendly and energy-efficient dwellings.
Flexibility and adaptability in codes for alternative housing options
To accommodate the growing popularity of alternative housing options like tiny homes, building codes need to embrace flexibility and adaptability. This means being open to alternative construction methods and designs that may deviate from traditional norms. By allowing for innovative approaches within the framework of the codes, regulatory authorities can support the development of diverse housing options while maintaining essential safety and quality standards.
In conclusion, building codes play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, quality, and sustainability of tiny homes. These codes address the unique challenges of building and living in tiny homes while ensuring consistency and standardization across different jurisdictions. By understanding and complying with building codes, builders and homeowners can create and enjoy safe, durable, and energy-efficient tiny homes. Organizations and resources specializing in tiny home codes can provide valuable guidance throughout the construction process, while proposed changes and advancements in codes for tiny homes pave the way for a more inclusive and sustainable housing future.